20 Financial Terms You Need to Know
Simply knowing these terms will help you manage your money more wisely


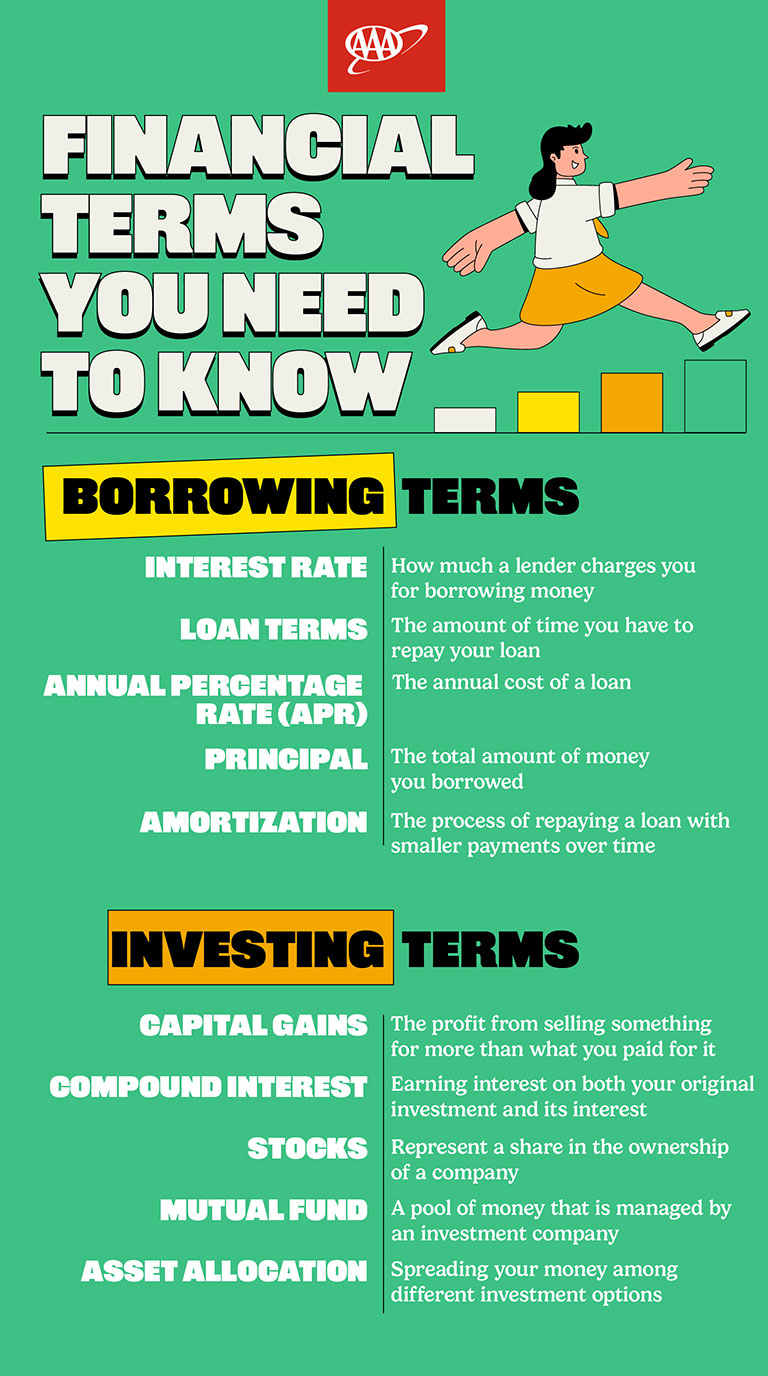
Financial jargon can seem like a whole new language. But knowing key financial terms can really change how you manage and think about your money. Once you understand what these terms mean, you’ll feel more confident and informed when making financial decisions. Whether you’re reading a loan agreement or comparing interest rates, here are some financial terms every adult should know.

Lending terms
Familiarity with lending terms is helpful when comparing your borrowing options. When you understand interest rates and loan terms, you’re in a better position to navigate the process.
Interest rate
This is how much a bank, lender, or creditor charges you for borrowing money, typically expressed as a percentage of the loan amount. Conversely, you can also earn interest when you save money in an interest-earning checking or savings account, as banks treat your deposit as a loan from you.
Annual percentage rate (APR)
This is another way interest rates are expressed. The APR represents the annual cost of a loan, including both the interest rate and any fees charged by the lender.
Loan terms
This refers to the amount of time you have to repay your loan. For example, mortgage lenders may offer terms of 30 years or 15 years, while car loans may range from 24 months to 96 months.
Principal
This is the amount of money you originally borrowed, excluding interest. For loans such as mortgages or student loans, the principal refers to the total amount of money you borrowed. As you make payments, parts of each payment goes toward reducing the principal, along with interest and fees.
Amortization
This refers to the process of gradually paying off a loan through regular payments over time. Each payment is typically divided into two parts: One part goes toward reducing the money you borrowed (the principal), and the other part covers the interest charged by the lender. Many banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions provide amortization schedules to show you how the loan will be paid off over time. These schedules typically detail how much of each payment goes toward interest and how much reduces the principal balance.

Investing terms
Getting to know investing terms can streamline your money management efforts and help you invest more confidently.
Capital gains
If you sell something, such as a stock, for more than what you paid for it, the profit you make is called a capital gain. Keep in mind that some of this profit may be taxed as capital gains tax, which can be as high as 20 percent.
Compound interest
Think of compound interest as interest earned on both your original investment and the interest you've already accumulated. It allows your money to grow faster over time. You can use a compound interest calculator to see how your investment can grow.
Stock
Stocks (also called shares) represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a partial owner and may share in its profits and any increase in its value.
Mutual fund
A mutual fund is a pool of money collected by many investors to invest in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and other securities. When you buy into a mutual fund, you own a share of the fund and earn a portion of its profits, based on its performance.
Asset allocation
Also known as diversification, asset allocation involves spreading out your money among different types of investments, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. The mix of investments you choose is based on your goals, risk tolerance, and how long you plan to invest. By diversifying, you reduce the risk of losing all your money if one investment performs poorly since other investments may help balance the loss.

Banking terms
Here are some key banking terms to help make it easier to navigate and use your accounts.
Overdraft protection
If you spend more money than is available in your account, it becomes overdrawn. Overdraft protection helps by linking another account, such as a savings account or a line of credit, to cover the shortfall. This can save you from paying extra fees if you accidentally spend more than you have in your checking account.
Hold
When you deposit a check, the bank may place a hold on the funds, meaning it will take some time before the money is available for use. This usually happens with check deposits, but cash deposits, wire transfers, and electronic payments generally don't have the same delays.
Electronic funds transfer (EFT)
An EFT is a digital transfer of money from one account to another. You usually see EFTs for things such as paying bills, receiving direct deposits, or setting up automatic payments.

Credit terms
Understanding credit basics helps you make informed borrowing decisions and manage your credit responsibly. Here are some key financial terms to know.
Credit report
Your credit report is like a report card for how you manage your finances. It details your financial and credit activity. Credit bureaus such as Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax collect this information from banks and lenders. By practicing good spending and credit habits—such as paying your bills on time—you can build a positive credit history.
Credit score
A credit score is a three-digit number, typically between 300 and 850, that reflects how well you manage credit. Lenders and financial institutions use this score to decide whether to approve your loan, what interest rate to offer, and the terms of the loan. FICO and VantageScore are the two most common scoring models. A score above 670 is generally considered good. The higher your score, the better your chances of securing lower rates and more favorable loan terms.

Financial planning terms
Understanding key financial planning terms can help you make informed decisions about managing your money. Here are some key financial terms.
Asset
An asset is anything that holds value, such as your investment accounts, property, cars, and valuables such as jewelry.
Liability
This is the amount of money you or an organization owes to someone else, such as a bank. Examples include car loans, mortgages, and other types of debt.
Net worth
Your net worth is the value of what you own (your assets) minus what you owe (liabilities). To calculate your net worth, simply add up all your money, investments, and property, and then subtract your debts, such as loans and credit cards. For example, if you own a $500,000 home outright, have $60,000 in investments, and a $20,000 car loan, your net worth would be $540,000.
Beneficiary
This is someone you designate to receive proceeds or property from your accounts, such as a 401(k) or life insurance policy, if you pass away.
Adjusted gross income (AGI)
This is your total income, minus certain deductions allowed by the IRS. These deductions might include things such as student loan interest, retirement contributions, or work-related expenses.
. . . . .
Knowledge is a powerful tool, especially when it comes to learning how to manage your money. Whether you're looking into car loans, planning for retirement, or building credit, getting familiar with these financial terms can help you feel more confident and make better financial decisions.
